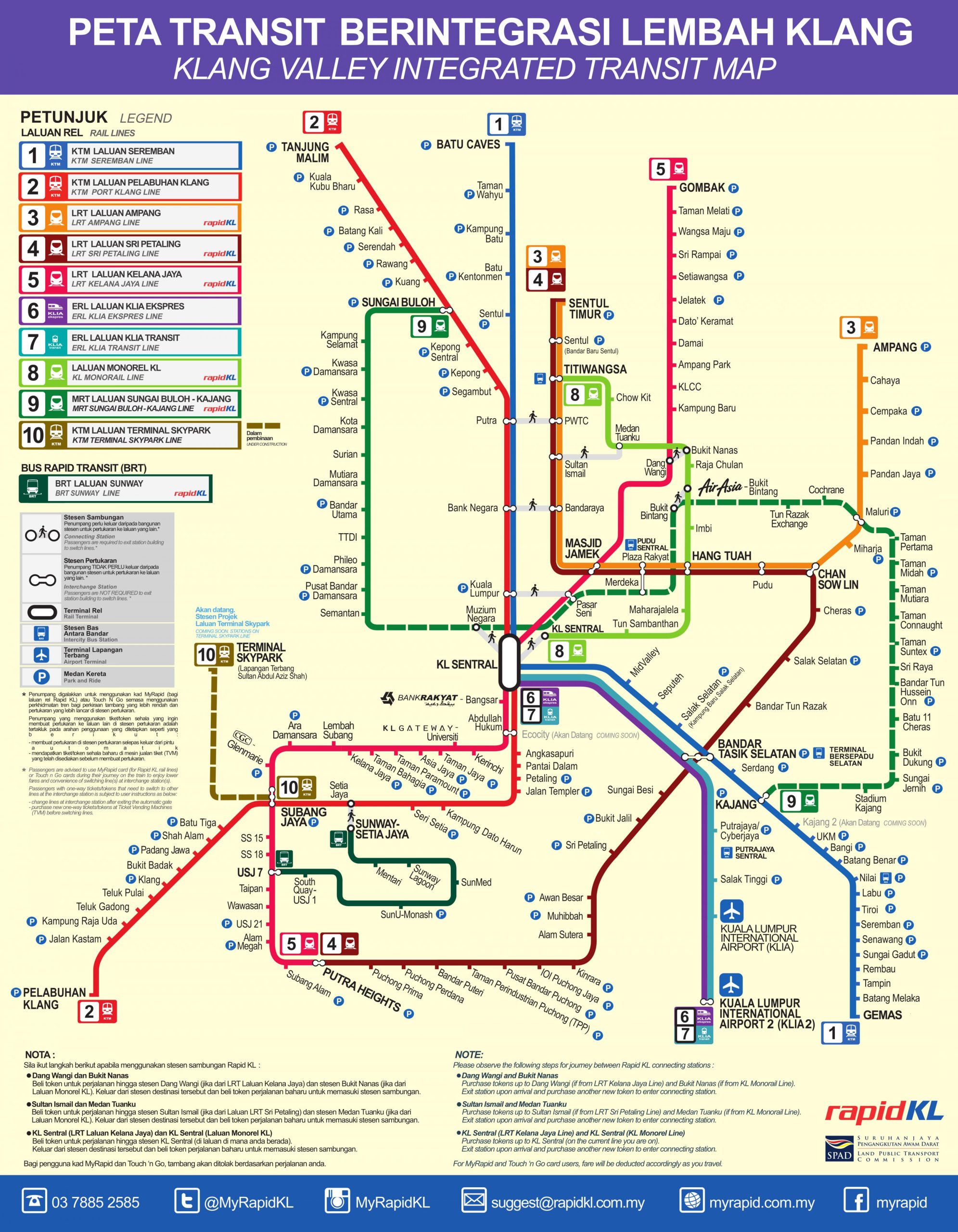
Kuala Lumpur’s Light Rail Transit system
Kuala Lumpur’s Light Rail Transit system consists of three light rail lines, one monorail, one commuter rail system consisting two lines, and two high-speed airport rail links.
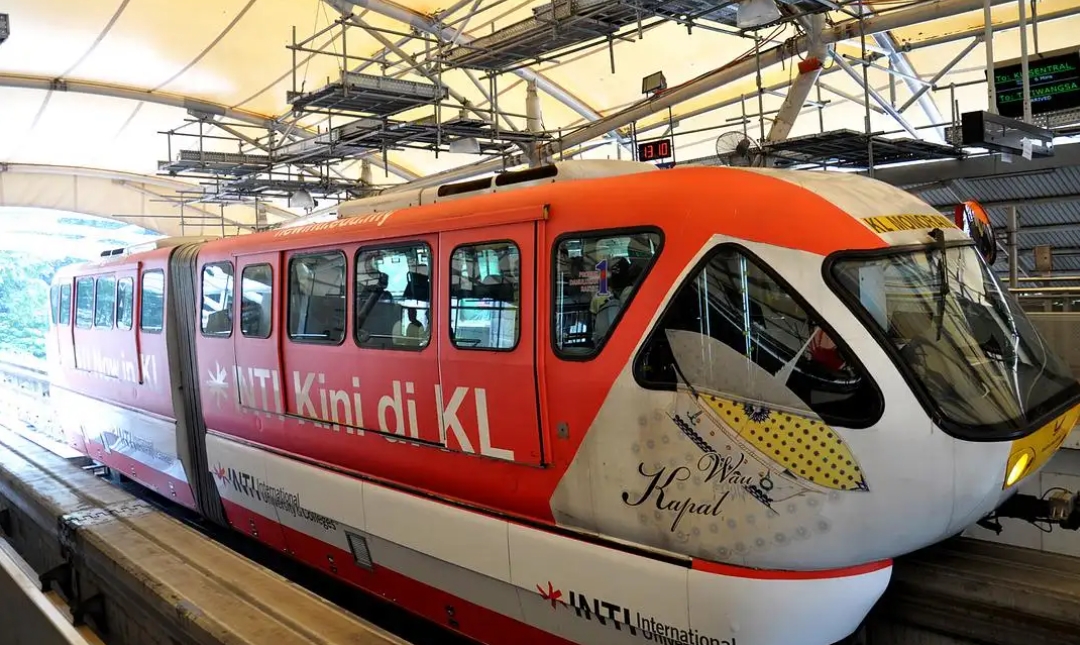

The three lines used by the LRT are Ampang Line, Kelana Jaya Line and Sri Petaling Line. The two commuter rail lines, known as KTM Komuter are the Sentul-Port Klang Line and the Rawang-Seremban Line. The sole monorail line is known as the Kuala Lumpur Monorail. The high speed KLIA Ekspres and KLIA Transit lines connect Kuala Lumpur to the international airport. Passengers holding KLIA Transit tickets are allowed to check-in luggage for several airlines at
the KL CAT in KL Sentral.
Different companies operate the various systems and developed them separately at different times. As a result, many of the lines do not integrate well, making transferring from system to system inconvenient for passengers. Moving from one system to another often require a lot of walking, stair-climbing, escalator-use and even crossing busy roads. For example, the KL Monorail’s “KL Sentral” station is a 140 m walk away through a busy bazaar and a busy road.
There is also no common ticket for all systems, forcing commuters on continuing journeys to buy new tickets when transferring. However, the LRT, monorail, and commuter rail systems now accept the Touch ‘n Go stored value fare card, easing the hassle.
The monorail is also planning to build a few more stations and tracks which is the Sungai Buloh Line (continued after Titiwangsa), Subang Jaya Line, Cheras Line and one other line that has yet to be decided on.
Network map of the Kuala Lumpur Rail Transit
Kelana Jaya Line
Between Terminal Putra to Kelana Jaya
23 stations over 29 km
Operated by Rapid KL, it was formerly known as PUTRA Line LRT system or simply PUTRA LRT. The system, is the third longest fully-automated driverless metro system in the world. it carries over 170,000 passengers a day and over 350,000 a day during national events.
Ampang Line
Between Sentul Timur and Ampang
18 stations over 15 km.
Operated by Rapid, the line runs between Sentul Timur in the north and Ampang in the east of Kuala Lumpur. It has 18 stations including the two end stations.
Commuters travelling from the Ampang direction and heading towards Sri Petaling can easily transfer at Chan Sow Lin because it is a cross-platform transfer. Trains are also timed to meet each other, cutting waiting time to a minimum.
Rawang-Seremban Line
Between Rawang and Seremban
23 stations over 153 km
operated by KTMB, this line caters especially to commuters in Kuala Lumpur and the surrounding suburban areas.
Transfers to Sentul-Port Klang Line can be done at KL Sentral, Kuala Lumpur and Putra stations. Stair-climbing or escalator-use may be required at KL Sentral and Putra, while cross-platform transfers can be conveniently done at Kuala Lumpur station.
KLIA Ekspres
From KL Sentral to KLIA
Non-stop over 75 km
Operated by ERL, which began its operations on 14 April 2002. The service runs along the Express Rail Link, and shares the line with KLIA Transit, which stops at all stations along the line.
Operating from 5 am to midnight, it takes around 28 minutes with the trains departing at 15-minute intervals during peak hours and 20-minute intervals during off-peak hours.
Sri Petaling Line
Between Sentul Timur and Sri Petaling
18 stations over 15 km,
Operated by Rapid KL and formerly known as Star-LRT, the line runs between Sentul Timur in the north and Sri Petaling in the southern part of Kuala Lumpur.
The Sri Petaling Line and Ampang Line share the same tracks between Sentul Timur and Chan Sow Lin stations, where they diverge. At the common stations, trains to Sri Petaling and those to Ampang arrive alternately
Sentul-Port Klang Line
Between Sentul and Port Klang
22 stations over 153 km
Operated by KTMB, this electrified commuter train service first introduced in 1995, caters especially to commuters in Kuala Lumpur and the surrounding suburban areas. It is a popular mode of transportation for commuters working in Kuala Lumpur, as they can travel to the city without the hassle of traffic congestion.
Transfers to Rawang-Seremban Line can be done at KL Sentral, Kuala Lumpur and Putra stations
KL Monorail
Between KL Sentral and Titiwangsa
11 stations over 8.6 km
Operated by KL Infrastructure it was opened 31 August 2003, running with two parallel elevated tracks, Iit connects Kuala Lumpur’s main station KL Sentral with the “Golden Triangle”.
The system utilises permanently coupled 2-car trains, which are able to accommodate 158 passengers each during regular operations. ridership is currently averaging 45,000 passengers per day
KLIA Transit
Between KL Sentral and KLIA
5 stations over 75 km
Pperated by ERL, it shares the same tracks as the KLIA Ekspres but unlike the direct airport express service, KLIA Transit stops at three other stations.








